Table of Contents
sim_isp_orig
This simulation is the adapted from the network used to generate Figure 4 in [1]. It simulates a balanced network of 10,000 sparsely connected integrate-and-fire neurons[2] and features plastic inhibitory-exciatory synapses.
[1] Vogels, T.P., Abbott, L.F., 2005. Signal propagation and logic gating in networks of integrate-and-fire neurons. J Neurosci 25, 10786. PubMed
[2] Vogels, T.P., Sprekeler, H., Zenke, F., Clopath, C., Gerstner, W., 2011. Inhibitory Plasticity Balances Excitation and Inhibition in Sensory Pathways and Memory Networks. Science 334, 1569 –1573. PubMed
Running the program
To run the program after compilation it suffices to call it as follows
./sim_isp_orig
this will trigger a 1000s simulation which creates the following output files
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 954 Jan 20 10:52 out.0.log 5456 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 5555044 Jan 20 10:52 out.0_e.ras 1412 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 1433909 Jan 20 10:52 out.0_i.ras 936 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 951025 Jan 20 10:52 out.0.volt 888 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 901395 Jan 20 10:52 out.0.ampa 928 -rw-r--r-- 1 zenke lcn1 942420 Jan 20 10:52 out.0.gaba
To see inhibitory plasticity in action the network can be initialized with small inithal I-E inhibitory weights. Try running the network with the following parameter
./sim_isp_orig --winh 0.01
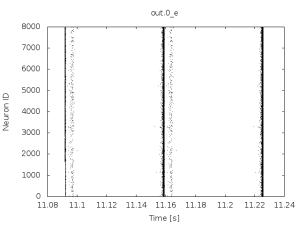
if you then plot the spiking activity recorded in out.0_e.ras after a couple of seconds it will look highly synchronous and pathologic as in the following
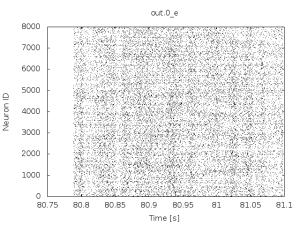
if you wait for roughly a minute this type of activity will give way to asynchronous irregular activity of the following type
Running in parallel
This version of the simulation can be run in parallel like any other Auryn simulation. See Running simulations in parallel for details.
The important bits
The following snipped of code first initializes two NeuronGroups of type TIFGroup and then initializes the neuronal membrane potentials to random values that follow a Gaussian distribution centered at -60mV with a standard deviation of 5mV. It furthermore creates an array of Poisson neurons called PoissonGroup, before moving on to set up the inhibitory and excitatory connections. Note that the connections from the inhibitory to the excitatory population is of type SymmetricSTDPConnection which implements inhibitory synaptic plasticity as specified in Vogels et al. 2011.
logger->msg("Setting up neuron groups ...",PROGRESS,true); TIFGroup * neurons_e = new TIFGroup(NE); TIFGroup * neurons_i = new TIFGroup(NI); neurons_e->random_mem(-60e-3,5e-3); neurons_i->random_mem(-60e-3,5e-3); PoissonGroup * poisson = new PoissonGroup(NP,poisson_rate); logger->msg("Setting up connections ...",PROGRESS,true); SparseConnection * con_ei = new SparseConnection(neurons_e,neurons_i,wei*w,sparseness,GLUT); SparseConnection * con_ii = new SparseConnection(neurons_i,neurons_i,gamma*w,sparseness,GABA); SparseConnection * con_exte = new SparseConnection(poisson,neurons_e,0,sparseness_afferents,GLUT); SparseConnection * con_ee = new SparseConnection(neurons_e,neurons_e,w,sparseness,GLUT); SymmetricSTDPConnection * con_ie = new SymmetricSTDPConnection(neurons_i,neurons_e, gamma*w,sparseness, gamma*eta,kappa,tau_stdp,wmax, GABA);
Note also that in the above code the PoissonGroup is connected with zero weights only. Certain of the these random sparse zero weights can be changed to non-zero values later in the simulation thus providing external input to the network. By default external input is given by external input currents and the PoissonGroup is simply dragged along (it would indeed be more efficient to not define it at all in this case). The actual setting up of a stimulus happens here
// stimulus if (!stimfile.empty()) { char ch; NeuronID counter = 0; ifstream fin(stimfile.c_str()); while (!fin.eof() && counter<NE) { ch = fin.get(); if (ch == '1') { if (poisson_stim==true) { for (int i = 0 ; i < NP ; ++i) con_exte->set(i,counter,w_ext); } else { neurons_e->set_bg_current(counter,chi*bg_current); } } counter++; } fin.close(); }
To run the network and keep activity alive even in the case of highly synchronized activity all cells in the network receive depolarizing external currents. This is set up here
for ( int j = 0; j < NE ; j++ ) { neurons_e->set_bg_current(j,bg_current); } for ( int j = 0; j < NI ; j++ ) { neurons_i->set_bg_current(j,bg_current); }
note however that set_bg_current is not a generic function of NeuronGroup, but a pecularity of the neuron model implemented as TIFGroup. To give currents to arbitrary NeuronGroups a CurrentInjector has to be used.
The full program
/* * Copyright 2014 Friedemann Zenke * * This file is part of Auryn, a simulation package for plastic * spiking neural networks. * * Auryn is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * Auryn is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with Auryn. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ #include <iomanip> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string> #include <iterator> #include <boost/program_options.hpp> #include "auryn_global.h" #include "auryn_definitions.h" #include "System.h" #include "Logger.h" #include "NeuronGroup.h" #include "TIFGroup.h" #include "PoissonGroup.h" #include "SparseConnection.h" #include "SymmetricSTDPConnection.h" #include "StateMonitor.h" #include "SpikeMonitor.h" #include "RateChecker.h" #define NE 8000 #define NI 2000 #define NP 1000 #define NSTIM 20 using namespace std; namespace po = boost::program_options; int main(int ac, char* av[]) { double w = 0.3 ; double w_ext = w ; double gamma = 10. ; double wmax = 10*gamma*w; double sparseness = 0.02 ; double eta = 1e-4 ; double kappa = 3. ; double tau_stdp = 20e-3 ; bool stdp_active = true; bool poisson_stim = false; double winh = -1; double wei = 1; double chi = 10.; double bg_current = 2e-2; double poisson_rate = 100.; double sparseness_afferents = 0.05; bool quiet = false; double simtime = 1000. ; NeuronID record_neuron = 30; // handle command line options string infilename = ""; string outputfile = "out"; string stimfile = ""; string strbuf ; int errcode = 0; try { po::options_description desc("Allowed options"); desc.add_options() ("help", "produce help message") ("quiet", "quiet mode") ("load", po::value<string>(), "input weight matrix") ("out", po::value<string>(), "output filename") ("stimfile", po::value<string>(), "stimulus file") ("eta", po::value<double>(), "learning rate") ("kappa", po::value<double>(), "target rate") ("simtime", po::value<double>(), "simulation time") ("active", po::value<bool>(), "toggle learning") ("poisson", po::value<bool>(), "toggle poisson stimulus") ("winh", po::value<double>(), "inhibitory weight multiplier") ("wei", po::value<double>(), "ei weight multiplier") ("chi", po::value<double>(), "chi current multiplier") ; po::variables_map vm; po::store(po::parse_command_line(ac, av, desc), vm); po::notify(vm); if (vm.count("help")) { cout << desc << "\n"; return 1; } if (vm.count("quiet")) { quiet = true; } if (vm.count("load")) { cout << "input weight matrix " << vm["load"].as<string>() << ".\n"; infilename = vm["load"].as<string>(); } if (vm.count("out")) { cout << "output filename " << vm["out"].as<string>() << ".\n"; outputfile = vm["out"].as<string>(); } if (vm.count("stimfile")) { cout << "stimfile filename " << vm["stimfile"].as<string>() << ".\n"; stimfile = vm["stimfile"].as<string>(); } if (vm.count("eta")) { cout << "eta set to " << vm["eta"].as<double>() << ".\n"; eta = vm["eta"].as<double>(); } if (vm.count("kappa")) { cout << "kappa set to " << vm["kappa"].as<double>() << ".\n"; kappa = vm["kappa"].as<double>(); } if (vm.count("simtime")) { cout << "simtime set to " << vm["simtime"].as<double>() << ".\n"; simtime = vm["simtime"].as<double>(); } if (vm.count("active")) { cout << "stdp active : " << vm["active"].as<bool>() << ".\n"; stdp_active = vm["active"].as<bool>(); } if (vm.count("poisson")) { cout << "poisson active : " << vm["poisson"].as<bool>() << ".\n"; poisson_stim = vm["poisson"].as<bool>(); } if (vm.count("winh")) { cout << "inhib weight multiplier : " << vm["winh"].as<double>() << ".\n"; winh = vm["winh"].as<double>(); } if (vm.count("wei")) { cout << "ei weight multiplier : " << vm["wei"].as<double>() << ".\n"; wei = vm["wei"].as<double>(); } if (vm.count("chi")) { cout << "chi multiplier : " << vm["chi"].as<double>() << ".\n"; chi = vm["chi"].as<double>(); } } catch(exception& e) { cerr << "error: " << e.what() << "\n"; return 1; } catch(...) { cerr << "Exception of unknown type!\n"; } // BEGIN Global definitions mpi::environment env(ac, av); mpi::communicator world; communicator = &world; stringstream oss; oss << outputfile << "." << world.rank(); outputfile = oss.str(); oss << ".log"; string logfile = oss.str(); logger = new Logger(logfile,world.rank()); sys = new System(&world); // END Global definitions logger->msg("Setting up neuron groups ...",PROGRESS,true); TIFGroup * neurons_e = new TIFGroup(NE); TIFGroup * neurons_i = new TIFGroup(NI); neurons_e->random_mem(-60e-3,5e-3); neurons_i->random_mem(-60e-3,5e-3); PoissonGroup * poisson = new PoissonGroup(NP,poisson_rate); logger->msg("Setting up connections ...",PROGRESS,true); SparseConnection * con_ei = new SparseConnection(neurons_e,neurons_i,wei*w,sparseness,GLUT); SparseConnection * con_ii = new SparseConnection(neurons_i,neurons_i,gamma*w,sparseness,GABA); SparseConnection * con_exte = new SparseConnection(poisson,neurons_e,0,sparseness_afferents,GLUT); SparseConnection * con_ee = new SparseConnection(neurons_e,neurons_e,w,sparseness,GLUT); SymmetricSTDPConnection * con_ie = new SymmetricSTDPConnection(neurons_i,neurons_e, gamma*w,sparseness, gamma*eta,kappa,tau_stdp,wmax, GABA); if (!infilename.empty()) { sys->load_network_state(infilename); } if (winh>=0) con_ie->set_all(winh); logger->msg("Setting up monitors ...",PROGRESS,true); strbuf = outputfile; strbuf += "_e.ras"; SpikeMonitor * smon_e = new SpikeMonitor( neurons_e , strbuf.c_str() ); strbuf = outputfile; strbuf += "_i.ras"; SpikeMonitor * smon_i = new SpikeMonitor( neurons_i, strbuf.c_str() ); smon_i->set_offset(NE); strbuf = outputfile; strbuf += ".volt"; StateMonitor * vmon = new StateMonitor( neurons_e, record_neuron, "mem", strbuf.c_str() ); strbuf = outputfile; strbuf += ".ampa"; StateMonitor * amon = new StateMonitor( neurons_e, record_neuron, "g_ampa", strbuf.c_str() ); strbuf = outputfile; strbuf += ".gaba"; StateMonitor * gmon = new StateMonitor( neurons_e, record_neuron, "g_gaba", strbuf.c_str() ); RateChecker * chk = new RateChecker( neurons_e , 0.1 , 1000. , 100e-3); for ( int j = 0; j < NE ; j++ ) { neurons_e->set_bg_current(j,bg_current); } for ( int j = 0; j < NI ; j++ ) { neurons_i->set_bg_current(j,bg_current); } // stimulus if (!stimfile.empty()) { char ch; NeuronID counter = 0; ifstream fin(stimfile.c_str()); while (!fin.eof() && counter<NE) { ch = fin.get(); if (ch == '1') { if (poisson_stim==true) { for (int i = 0 ; i < NP ; ++i) con_exte->set(i,counter,w_ext); } else { neurons_e->set_bg_current(counter,chi*bg_current); } } counter++; } fin.close(); } logger->msg("Simulating ...",PROGRESS,true); con_ie->stdp_active = stdp_active; sys->run(simtime); logger->msg("Saving network state ...",PROGRESS,true); sys->save_network_state(outputfile); logger->msg("Freeing ...",PROGRESS,true); delete sys; logger->msg("Exiting ...",PROGRESS,true); return errcode; }